

(b) I 2 ( a q ) + I − ( a q ) ⇌ I 3 − ( a q ) − x − x x I 2 ( a q ) + I − ( a q ) ⇌ I 3 − ( a q ) − x − x x

(a) C 2 H 2 ( g ) + 2 Br 2 ( g ) ⇌ C 2 H 2 Br 4 ( g ) x 2 x − x C 2 H 2 ( g ) + 2 Br 2 ( g ) ⇌ C 2 H 2 Br 4 ( g ) x 2 x − x (b) I 2 ( a q ) + I − ( a q ) ⇌ I 3 − ( a q ) _ _ x I 2 ( a q ) + I − ( a q ) ⇌ I 3 − ( a q ) _ _ x These terms are derived from the stoichiometry of the reaction, as illustrated by decomposition of ammonia:ĭetermining Relative Changes in Concentrationĭerive the missing terms representing concentration changes for each of the following reactions.
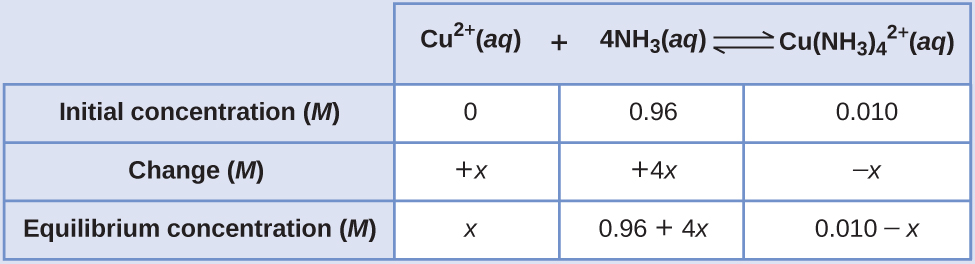
Many of the useful equilibrium calculations that will be demonstrated here require terms representing changes in reactant and product concentrations. Knowledge of the quantitative aspects of these equilibria is required to compute a dosage amount that will solicit the desired therapeutic effect. After a drug is ingested or injected, it is typically involved in several chemical equilibria that affect its ultimate concentration in the body system of interest. These types of computations are essential to many areas of science and technology-for example, in the formulation and dosing of pharmaceutical products.

Having covered the essential concepts of chemical equilibria in the preceding sections of this chapter, this final section will demonstrate the more practical aspect of using these concepts and appropriate mathematical strategies to perform various equilibrium calculations.
Calculate equilibrium concentrations or pressures and equilibrium constants, using various algebraic approaches. Identify the changes in concentration or pressure that occur for chemical species in equilibrium systems. Or, if you want to save time on your thermodynamics homework, enter an equation to calculate the enthalpy of any reaction in seconds!Īdditionally, you can quickly search for element data, compound names and formulas, polyatomic ions, thermodynamic quantities, and acid/base dissociation constants.By the end of this section, you will be able to: On top of that, it'll do your stoichiometry for you in less than a minute! You can find the limiting reactant for a given reaction, the amount of excess reactant left, as well as the theoretical yield! The app uses algorithms to calculate the molar mass of any chemical compound, with easy converting between grams and moles.ĬhemCalc can also balance chemical equations using a complex matrix algorithm, allowing you to double-check your work and recognize reaction patterns. searchable lists of compound formulas, polyatomic ions, and thermodynamic quantitiesĪs of 2021, ChemCalc is the only app on the App Store that can solve ICE tables to calculate equilibrium concentrations! Quickly enter in the chemical equation, equilibrium constant, and initial concentration, and you'll be able to verify your answers to those long equilibrium problems. colorful table of elements with extensive element data. standard enthalpy/entropy/spontaneity calculator. ICE table solver for equilibrium problems. ChemCalc is an all-in-one calculator and reference guide for high school and college chemistry. Struggling in your first chemistry class? Is stoichiometry too time-consuming and difficult for you? Or maybe you're tired of spending 30 minutes trying to figure out that ICE table problem.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
